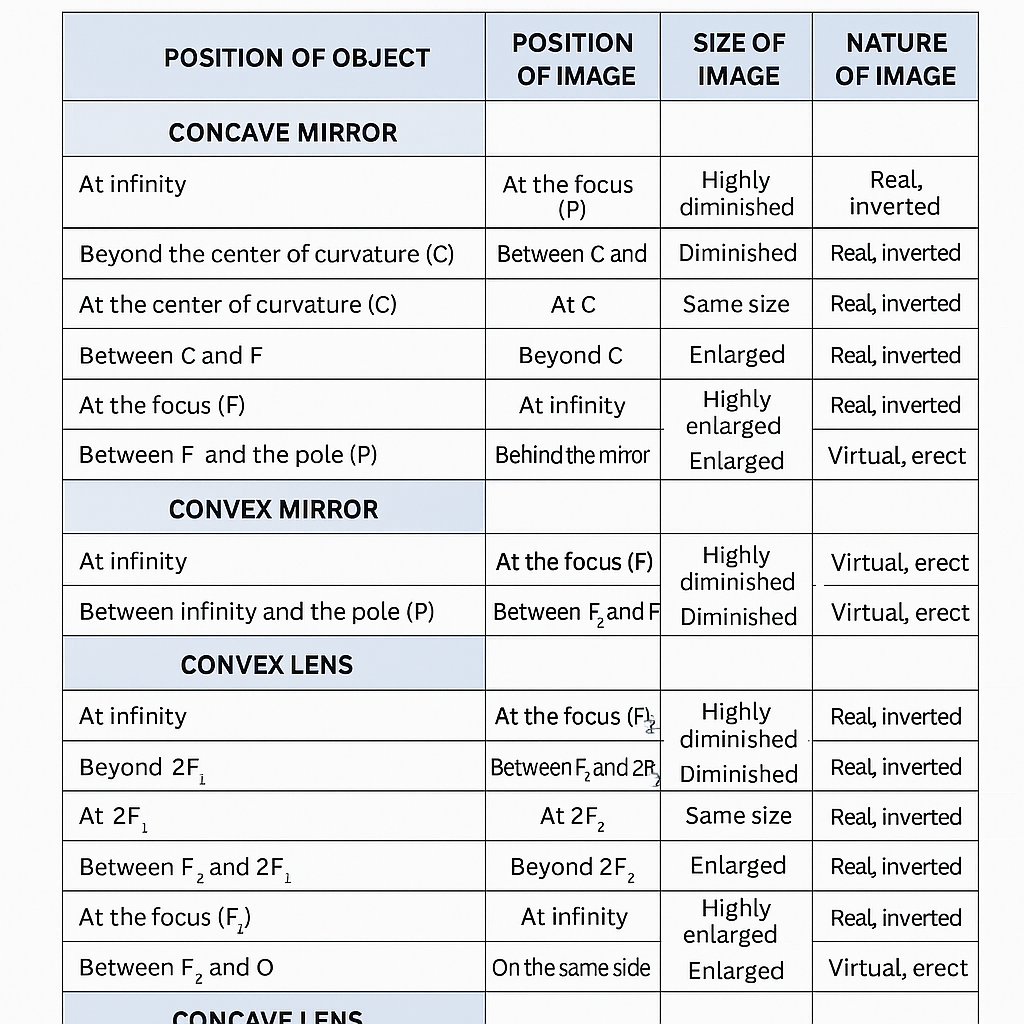
Grade X: Lens and Mirrors Image Formation Table
Understanding how images are formed by lenses and mirrors is a foundational concept in Grade X Physics. In this post, we present a detailed and structured explanation of image formation by concave and convex mirrors as well as converging (convex) and diverging (concave) lenses. This guide is designed to help students grasp the key principles with clarity and confidence, with SEO optimization to support better search visibility.
Image Formation by Concave Mirror
| Object Position | Image Position | Image Nature |
|---|---|---|
| At infinity | At focus (F) | Real, inverted, highly diminished |
| Beyond C | Between F and C | Real, inverted, diminished |
| At C | At C | Real, inverted, same size |
| Between C and F | Beyond C | Real, inverted, magnified |
| At focus (F) | At infinity | Real, inverted, highly magnified |
| Between pole and focus | Behind mirror | Virtual, erect, magnified |
Image Formation by Convex Mirror
| Object Position | Image Position | Image Nature |
|---|---|---|
| At any position | Behind mirror (between pole and focus) | Virtual, erect, diminished |
Image Formation by Convex Lens
| Object Position | Image Position | Image Nature |
|---|---|---|
| At infinity | At focus on opposite side | Real, inverted, highly diminished |
| Beyond 2F | Between F and 2F | Real, inverted, diminished |
| At 2F | At 2F | Real, inverted, same size |
| Between F and 2F | Beyond 2F | Real, inverted, magnified |
| At focus (F) | At infinity | Real, inverted, highly magnified |
| Between pole and focus | Same side as object | Virtual, erect, magnified |
Conclusion
These tables provide a structured overview of how different object positions affect image characteristics when using lenses and mirrors. Mastering these concepts is crucial for success in Grade X Physics and forms the foundation for more advanced optical studies. Bookmark this page and revisit whenever you need a quick revision or deeper understanding of image formation principles.